The Swedish higher education system
A good place to start in your search for information about studying in Sweden is to learn some basics about how the academic system here works.

Preschool to upper secondary
Education in Sweden is mandatory for children between the ages of 6 and 15. Preschool, primary and lower secondary education are completed during this time.
Upper secondary education is optional, but required if a person wishes to study at the higher education level. There are a few ways you can prepare for your higher education studies:
- the higher education preparatory programme (Högskoleförberedande examen/Higher education preparatory diploma) has six national programmes and a general education content
- the vocational programme (Yrkesexamen/Vocational diploma) with 12 national programmes. The vocational diploma can give access to higher education only if supplemented with passing grades in specific courses in Swedish and English.
All upper secondary programmes are three years in length.
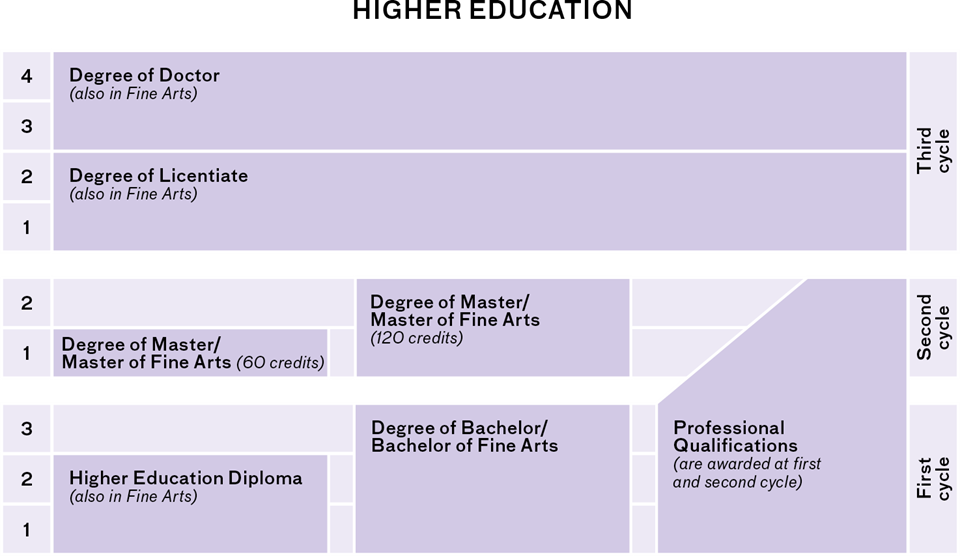
Higher education levels
Bachelor's level (First cycle)
Bachelor's level is also known as first cycle in the European Region. You may also be familiar with the term 'undergraduate'. In Sweden, there's a wide range of international courses available at this level, and a limited number of study programmes. These courses and programmes are taught in English. A student must have completed upper secondary studies that give access to higher education in order to be qualified for study at this level.
Master's level (Second cycle)
The next level is master's, also known as second cycle in the European Region. The term 'graduate level' can also be used. Universities in Sweden offer a large range of international master's programmes where the language of instruction is English. These programmes are open to both Swedish and international students who've earned a bachelor's degree (equivalent to a Swedish kandidatexamen).
Professional qualifications
Professional qualifications are awarded in the fields of engineering, health care, agriculture, law, education, etc. Professional qualifications may be offered within either the first or the second cycle. Programmes leading to professional qualifications may vary in length depending on their content and may stretch over two cycles.
Most often, a professional qualification takes 5 years of full-time studies to complete.
Doctoral level (Third cycle)
After having earned a master's degree, students have the possibility of continuing their university studies at the doctoral level. Students interested in studying at the doctoral level have a different admissions process than students studying at other levels. This process is coordinated by the universities; therefore, you must contact them directly for application instructions.
Contact information for universities
Academic year
The academic year is split into autumn and spring semesters. The majority of courses and programmes start in the autumn.
The autumn semester begins at the end of August and continues until mid-January of the following year. The spring semester usually starts in January and finishes at the end of June.
Between the spring and autumn semesters, many universities have a short summer session. A student may be awarded a maximum of 15 credits for courses taken during the summer session.
Courses or study programmes
When applying to study in Sweden, you may choose to apply for individual courses or full study programmes.
If you choose to study a freestanding course or range of courses, you're awarded credits on completion of these courses. It's possible to be awarded a diploma or degree if you accumulate the appropriate number of credits in the right combination.
You can also apply for a full study programme. Study programmes are made up of courses, some of which are required and some of which are optional. Some of the study programmes lead to professional or vocational qualifications. Study programmes vary in length from two to eleven semesters.
Credit system compatible with ECTS
A normal study workload is 30 higher education (HE) credits per semester or 60 HE credits per academic year.
ECTS - for recognition in European countries
ECTS stands for European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System. This is a system common in European countries and helps the recognition of higher education between countries.